Introduction
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) sit at the heart of nearly every modern device, from smartphones and laptops to cars and medical equipment. Their reliability directly impacts how well these products work over time. If a PCB fails, the entire system is at risk, which can mean anything from a small inconvenience to a serious safety issue.
For consumers, PCB reliability may not always be visible, but it matters more than you might think. This guide explains what PCB reliability is, what affects it, how it’s tested, and why it’s important for the products you use every day.
1. What PCB Reliability Really Means
PCB reliability is the ability of a circuit board to consistently perform its function without failure for its expected lifetime. In practical terms, it means the board can handle its electrical load, environmental conditions, and physical stress without breaking down.
For consumers, this translates to:
- Fewer device malfunctions
- Longer-lasting electronics
- Better overall value for money
A reliable PCB is one you never notice because your device keeps working smoothly.
2. Why PCB Reliability Matters for Everyday Products
When you buy a device, you expect it to work for years, not months. The reliability of the PCB inside plays a big role in meeting that expectation.
Here are a few examples:
- Automotive electronics: A weak PCB could cause critical systems like airbags or navigation to fail.
- Medical devices: Patient safety depends on circuits that perform consistently.
- Consumer electronics: Phones, laptops, and gaming systems with poor PCB reliability often overheat, freeze, or die prematurely.
In other words, PCB reliability isn’t just an engineering term. It directly affects your safety, convenience, and satisfaction as a consumer.
3. The Factors That Impact PCB Reliability
Not all PCBs are built the same way. Several factors determine how long they will last:
- Material quality: High-grade laminates, copper, and solder joints resist wear better.
- Design quality: Proper spacing, heat management, and layout choices prevent failures.
- Manufacturing standards: Precision in drilling, plating, and assembly reduces defects.
- Environmental exposure: Heat, moisture, vibration, and dust can shorten PCB lifespan.
- Usage conditions: Heavy workloads, high power levels, and constant use naturally stress boards more.
When manufacturers balance these factors correctly, they deliver boards that hold up under real-world conditions.
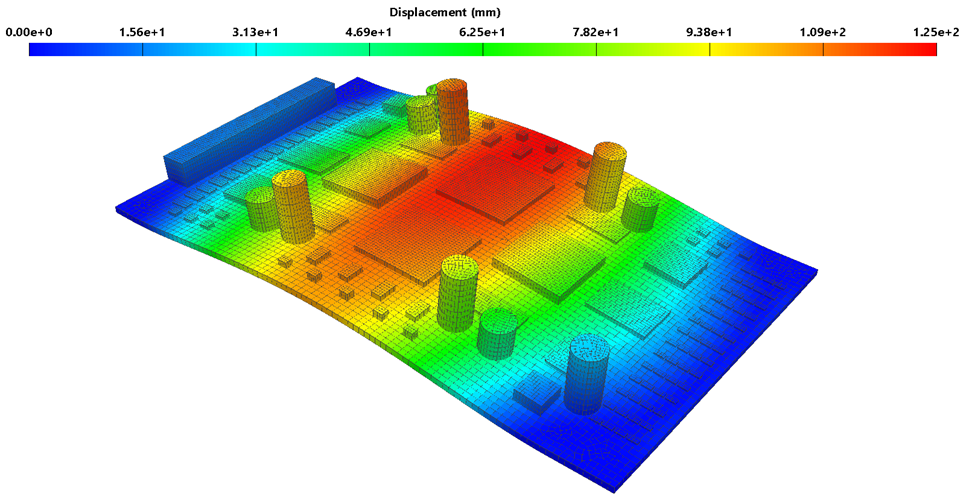
4. How Engineers Measure PCB Reliability
Reliability is not left to chance. Engineers use tests and predictive models to estimate how long a PCB will last:
- Accelerated stress testing: Exposing boards to high temperatures or vibration to simulate years of wear.
- Thermal cycling: Heating and cooling boards repeatedly to test solder joints and connections.
- Failure rate calculations: Using recognized models such as Telcordia or MIL-HDBK standards to estimate reliability.
- Field performance data: Reviewing real-world product use to confirm predictions.
These methods allow companies to predict failures before products reach consumers.
5. How Consumers Benefit from Reliable PCBs
Even though you don’t see the PCB inside your device, its reliability has a big impact on your experience. Reliable PCBs mean:
- Devices last longer and deliver better performance.
- Warranties are more trustworthy because manufacturers can stand behind their products.
- Fewer unexpected breakdowns that cost time and money to repair.
- Greater safety in critical applications like cars, healthcare devices, and home appliances.
For consumers, one of the simplest ways to check reliability is to look for products from reputable brands with strong warranties and quality certifications.
FAQs
What does PCB reliability mean in simple terms?
It’s how long a printed circuit board can keep working without failing.
Why is PCB reliability important to consumers?
Because it determines how long devices last and how safe they are.
What factors affect PCB reliability?
Material quality, design, manufacturing processes, and environmental stress.
How do engineers test PCB reliability?
Through stress tests like thermal cycling, vibration testing, and predictive models.
Can poor PCB reliability cause product failures?
Yes. It can lead to overheating, power issues, or complete system breakdowns.
Conclusion
PCB reliability may seem like a behind-the-scenes issue, but it’s one of the most important parts of product quality. Reliable boards make your devices last longer, perform better, and stay safe over time. For manufacturers, reliability testing builds trust and reduces costs. For consumers, it means better value and peace of mind when investing in electronics.
By understanding the basics of PCB reliability, you can make smarter choices about the products you buy and appreciate the engineering that keeps them running day after day.